Financial reporting is the backbone of corporate transparency and accountability in New Zealand. It provides stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and management, with insights into a company’s financial health. Accurate financial reporting is not just a regulatory obligation—it is a strategic tool that drives informed decision-making and business growth.
New Zealand businesses must comply with set financials standards set by the External Reporting Board (XRB) and Inland Revenue (IRD) to ensure accurate and reliable financial disclosures. This article explores the key aspects of financial reporting, including compliance requirements, best practices, and how businesses can leverage financial reports for success.
Understanding Financial Reporting in New Zealand
It involves preparing and presenting financial statements that provide a clear picture of a business’s financial position. The key financial statements include:
- Balance Sheet: Shows assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
- Income Statement: Details revenue, expenses, and net profit or loss over a period.
- Cash Flow Statement: Tracks cash inflows and outflows, helping businesses manage liquidity.
- Statement of Changes in Equity: Outlines changes in ownership interest and retained earnings.
In New Zealand, businesses must follow the New Zealand Generally Accepted Accounting Practice (NZ GAAP), ensuring that financial statements are prepared consistently and transparently.
Financial Reporting Compliance and Standards
The External Reporting Board (XRB) establishes financial reporting standards that businesses must adhere to, depending on their size and structure. Compliance requirements vary based on whether a company is a small business, a large entity, or a public interest entity.
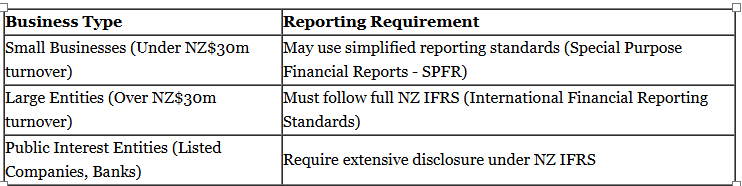
Failing to meet reporting obligations can result in penalties, financial loss, and damage to reputation. Businesses must ensure that they stay updated on reporting changes to maintain compliance.
Best Practices for Accurate Financial Reporting
1. Maintain Accurate and Up-to-Date Records
Keeping comprehensive financial records is the foundation of reliable reporting. Businesses should use accounting software to track transactions, expenses, and revenue accurately.
2. Conduct Regular Internal Audits
Internal audits help identify errors, fraud, and discrepancies before they become major issues. Conducting periodic financial reviews ensures that records align with business activities.
3. Ensure Timely Submission of Reports
Financial reports must be prepared and submitted within the required deadlines to avoid penalties and maintain compliance. Businesses should establish a structured reporting schedule to stay on track.
4. Seek Professional Guidance
This process can be complex, especially for businesses with multiple revenue streams. Engaging an accountant or financial expert ensures compliance with NZ GAAP and XRB standards while optimizing financial strategies.
The Role of Technology in Financial Reporting
Modern businesses leverage technology to streamline financial reporting processes. Cloud-based accounting software such as Xero simplifies data management, enhances accuracy, and allows real-time financial monitoring. Automation reduces human errors and increases efficiency in generating reports.
Conclusion
Financial reporting is more than a regulatory requirement—it is a strategic tool for business success. By ensuring accurate record-keeping, complying with reporting standards, and leveraging modern technology, businesses can improve transparency, attract investors, and make informed financial decisions.
For expert financial reporting assistance, Aurora Financials provides tailored solutions to help businesses meet compliance requirements and optimize financial performance. Contact us today to ensure your financial reports are accurate and compliant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why is financial reporting important for businesses in New Zealand?
It ensures transparency, regulatory compliance, and informed decision-making for business owners and stakeholders.
2. What happens if a business fails to comply with financial reporting standards?
Non-compliance can result in legal penalties, reputational damage, and potential audits from regulatory authorities.
3. What are the key financial statements required for reporting?
Businesses must prepare a balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of changes in equity.
4. Can small businesses use simplified financial reporting methods?
Yes, small businesses can use Special Purpose Financial Reports (SPFR) instead of full NZ IFRS standards.
5. How can technology improve financial reporting?
Cloud-based accounting software helps automate financial tracking, improves accuracy, and simplifies compliance processes.






