Every business that sells on credit needs to keep track of who owes them money and when it’s due. This is where Accounts Receivable Aging comes in. It helps business owners and accountants understand which customers have unpaid invoices and how long those invoices have been outstanding.
In this blog, we’ll break down what accounts receivable aging means, why it’s important, and how businesses use it to manage cash flow and reduce financial risk.
What Is Accounts Receivable Aging?
Accounts Receivable Aging, often called an A/R Aging Report, is a financial tool that shows unpaid customer invoices and groups them by how long they’ve been overdue.
Instead of just seeing the total amount owed, the aging report separates it by time periods. For example, it shows how much is owed that is:
- Not yet due
- 1–30 days overdue
- 31–60 days overdue
- 61–90 days overdue
- Over 90 days overdue
This breakdown helps businesses quickly see which invoices need attention and whether any customers are falling behind on payments.
Why Is It Called “Aging”?
The word “aging” refers to the time that has passed since the invoice date. The older an invoice becomes without being paid, the more likely it is to turn into a bad debt – money the business may never collect.
The goal of an aging report is to spot these old invoices early and take action before it’s too late.
Why Is Accounts Receivable Aging Important?
1. It Helps Manage Cash Flow
When a company knows exactly when it can expect payments, it can better plan its spending. If too much money is tied up in unpaid invoices, the business may struggle to pay its own bills.
2. It Identifies Problem Accounts
Some customers may consistently delay payments. The aging report shows patterns that help businesses decide whether to follow up more often, set stricter payment terms, or even stop offering credit to certain clients.
3. It Supports Better Decision-Making
Business owners and finance teams use aging reports to assess risk. If a large portion of receivables is overdue, it might be a red flag. This can impact decisions around hiring, purchasing, or seeking loans.
4. It Improves Collection Efforts
Aging reports help collection teams prioritize who to contact. Rather than chasing every customer, they can focus on those with older balances or large amounts due.
What Does an A/R Aging Report Include?
Although we’re avoiding tables, here’s what’s typically included in an aging report:
- Customer name
- Invoice number
- Invoice date
- Due date
- Amount owed
- How many days overdue
The system then groups the invoices into time categories (also called aging buckets). Many accounting software platforms like Xero, or QuickBooks can automatically generate these reports.
How Often Should Aging Be Reviewed?
Aging reports should be reviewed weekly or monthly, depending on the size of the business and the number of transactions.
Regular reviews help catch issues early and give businesses a chance to fix problems before they get worse.
How It Affects the Balance Sheet
Accounts receivable appears on the balance sheet as a current asset. However, if a large portion of it is overdue, it may not be easily converted to cash. This can weaken a company’s financial position, even though the amounts are still recorded as assets. In some cases, businesses must estimate how much of their receivables may never be collected. This estimate is called a bad debt allowance.
The aging report is a key tool in making that estimate.
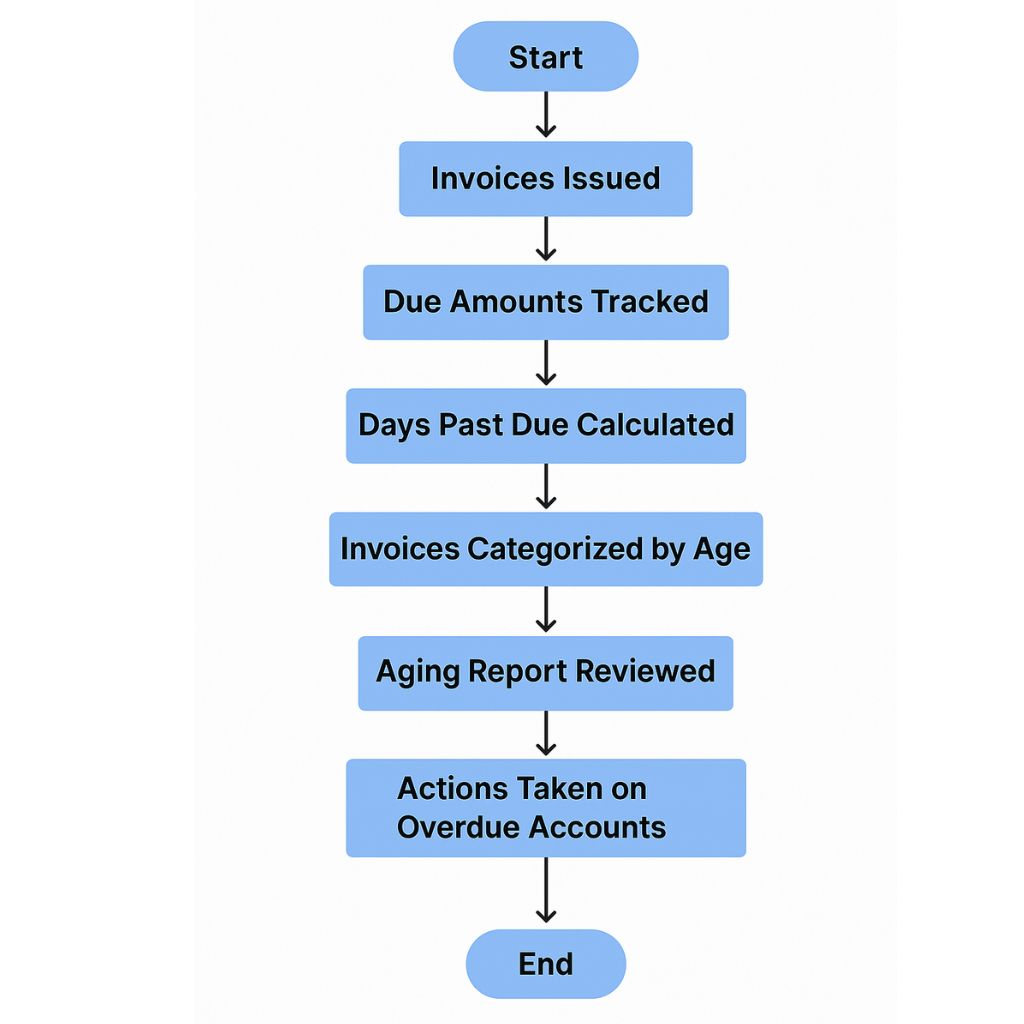
Steps to Create an Aging Report
- List All Unpaid Invoices
Include the customer’s name, invoice date, due date, and amount owed. - Calculate Days Overdue
Subtract the invoice due date from today’s date. - Group Into Aging Buckets
Categorize based on how many days the invoice is overdue. - Review and Take Action
Identify which customers need reminders, follow-up, or payment plans.
Most businesses use accounting software to automate this process.
What Happens When Receivables Get Too Old?
The older an invoice becomes, the harder it is to collect. At some point, the business may have to write it off as a bad debt.
To avoid this, businesses often set up credit policies, rules for who gets credit and how late payments are handled. These policies are usually supported by the insights gained from the accounts receivable aging report.
Tips for Managing A/R Aging
- Send invoices promptly after delivering goods or services.
- Offer payment reminders as the due date approaches.
- Follow up as soon as an invoice becomes overdue.
- Incentivize early payment with small discounts.
- Establish credit limits for customers with poor payment history.
- Use automation to save time and reduce errors.
Good management of accounts receivable aging keeps the cash flowing and strengthens business stability.
Final Thoughts
Accounts receivable aging may sound like a complex accounting term, but it’s simply a way to track who owes you money and how long they’ve owed it. It’s a powerful tool that helps businesses stay on top of their cash flow, avoid financial surprises, and reduce the risk of not getting paid.
By checking aging reports regularly and acting on them, businesses improve their chances of being paid on time and keeping their operations smooth.






